HTML에서 각 요소 레이어가 화면에 쌓이는 순서와 쌓이는 맥락(?)을 의미하는데,
아래 예제가 가장 유명한 듯 하다
<style>
/*div:first-child {*/
/* opacity: .99;*/
/*}*/
.red, .green, .blue {
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
color: white;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
.red {
z-index: 1;
top: 420px;
left: 20px;
background: red;
}
.green {
top: 460px;
left: 60px;
background: green;
}
.blue {
top: 500px;
left: 100px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
<div>
<span class="red">Red</span>
</div>
<div>
<span class="green">Green</span>
</div>
<div>
<span class="blue">Blue</span>
</div>
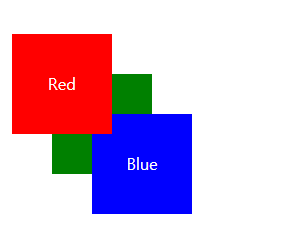
주석처리한 opacity를 활성화하면
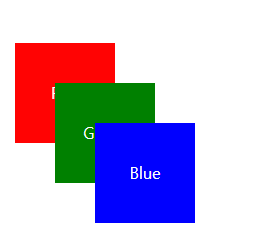
이렇게 된다.
stacking order인지 context떄문인지는 모르겠다.
다른 예제로 z-index를 활용한 예제가 있는데, 보다 명확하게 이해할 수 있을 것 같다.
(적어도 z-index를 활용한 부분에 대해서만큼은)
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
}
html {
padding: 20px;
font: 12px/20px Arial, sans-serif;
}
div {
opacity: 0.7;
position: relative;
}
h1 {
font: inherit;
font-weight: bold;
}
#div1,
#div2 {
border: 1px dashed #696;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #cfc;
}
#div1 {
z-index: 5;
margin-bottom: 190px;
}
#div2 {
z-index: 2;
}
#div3 {
z-index: 4;
opacity: 1;
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
left: 180px;
width: 330px;
border: 1px dashed #900;
background-color: #fdd;
padding: 40px 20px 20px;
}
#div4,
#div5 {
border: 1px dashed #996;
background-color: #ffc;
}
#div4 {
z-index: 6;
margin-bottom: 15px;
padding: 25px 10px 5px;
}
#div5 {
z-index: 1;
margin-top: 15px;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
#div6 {
z-index: 3;
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 180px;
width: 150px;
height: 125px;
border: 1px dashed #009;
padding-top: 125px;
background-color: #ddf;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<div id="div1">
<h1>Division Element #1</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 5;</code>
</div>
<div id="div2">
<h1>Division Element #2</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 2;</code>
</div>
<div id="div3">
<div id="div4">
<h1>Division Element #4</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 6;</code>
</div>
<h1>Division Element #3</h1>
<code>position: absolute;<br/>
z-index: 4;</code>
<div id="div5">
<h1>Division Element #5</h1>
<code>position: relative;<br/>
z-index: 1;</code>
</div>
<div id="div6">
<h1>Division Element #6</h1>
<code>position: absolute;<br/>
z-index: 3;</code>
</div>
</div>
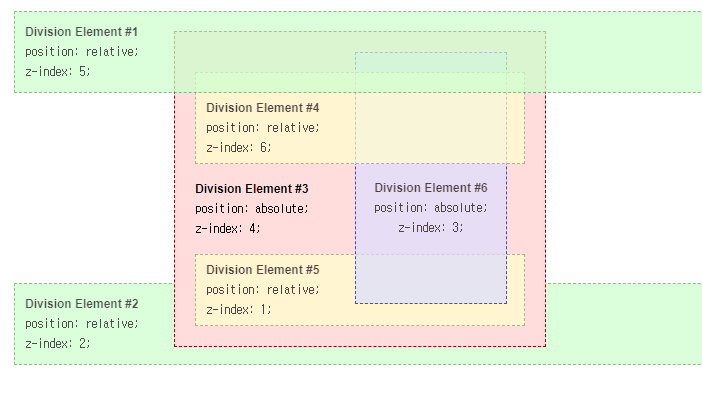
z-index값에 따라서 각 레이어가 쌓이는 것을 볼 수 있는데,
z-index가 div4가 div1보다 뒤에 있는 이유는 div4의 부모(div3)의 z-index가 div1보다 작은 값이기 때문이다.
또한, div6의 z-index를 0또는 그 이하로 작게 설정하더라도 부모 요소의 뒤로 이동하지는 않는다.
대략적인 내용을 봤을 때 이해한 내용을 요약하자면 다음과 같다.
1. stacking context는 root 요소(최상위 부모요소)를 기준으로 생성된다
2. stacking order는 stacking context가 동일한 위치에 있을 때, 이 요소들이 쌓이는 순서를 의미한다.
3. stacking order는 z-index가 있으면 그 값을 기준으로 쌓이고, 그렇지 않으면 html에 작성된 순서대로 쌓인다.
- 쌓임 맥락이 다른 쌓임 맥락을 포함할 수 있고, 함께 계층 구조를 이룹니다.
- 쌓임 맥락은 형제 쌓임 맥락과 완전히 분리됩니다. 쌓임을 처리할 땐 자손 요소만 고려합니다.
- 각각의 쌓임 맥락은 독립적입니다. 어느 요소의 콘텐츠를 쌓은 후에는 그 요소를 통째 부모 쌓임 맥락 안에 배치합니다.
반응형
'FrontEnd > CSS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| flexbox vs inline block (0) | 2024.07.18 |
|---|---|
| CSS 전처리기의 종류와 장단점 (0) | 2020.11.05 |

